이진트리(Binary Tree)란?
이진트리란?
우리가 트리라는 개념을 처음 접할때 이진 트리로 접한다. 사실 트리는 이진이든 삼진 사진 오진 개발자가 만들기 나름이다. 단지 우리가 개념을 보다 쉽게 접하기 위해, 짜기 편하기 때문에 이진트리로 배우는 것이다.
- 이진 트리는 자식을 최대 두개 가질 수 있는 자료구조이다.
- 짜기나름이지만 삽입할때 부모 노드보다 작으면 왼쪽, 크면 오른쪽에 넣는다.
- 전위 순회, 중위 순회, 후위 순회 등의 노드를 순회하는 방법이 있다.
- 삽입, 탐색시 시간복잡도가 O(log2(n))이다. but 최악은 O(n)이다.(한쪽 방향으로만 노드가 치우치는 경우 때문이다.)
예시
요즘 예시로 이런거 그릴 여유가 없네..
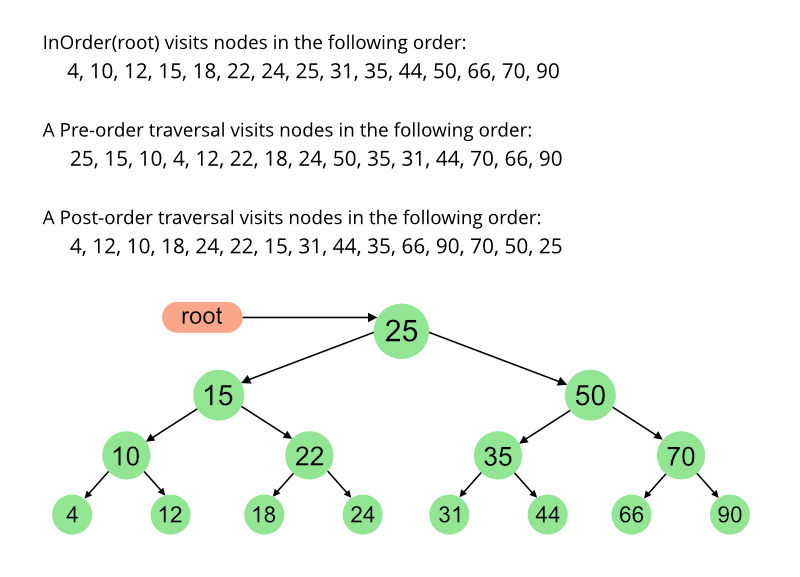
트리의 삽입은 위와 같이 부모 노드를 기준으로 작으면 왼쪽, 크면 오른쪽에 넣는다. 에..? 그럼 노드들이 정렬되는것도 아니고 일관성이 없지 않는가?(그렇다.. 이건 이진트리의 기본형태일뿐 이 형태를 이용해 향후 heap, avl 등을 배우게 될것이다.)
그리고 만약 원소를 찾는다고 하면 현재 원소가 부모노드보다 큰지 작은지에 따라 왼쪽으로 갈지 오른쪽으로 갈지 판단 해서 찾아가면 될것이다.
이진트리의 순회방식
이진트리에 순회방식이 있다. 어느 노드를 중점으로 순회하느냐에 따라 전위 순회, 중위 순회, 후위순회라고 불린다. 그렇게 중요한 개념은 아니지만 시험에 내기 좋은 문제다 =ㅅ=(그냥 방문 방식일뿐!) 이 세가지 방식은 모두 dfs방식이다.
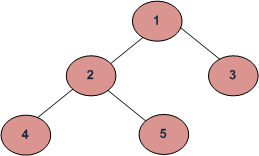
아래 사진을 예제로 해보자
전위 순회(preorder traversal)
root -> left -> right 순으로 탐색한다 left를 기점으로 삼각형을 그리며 탐색된다.
Inorder (Left, Root, Right) : 4 2 5 1 3
중위 순회(inorder traversal)
left -> root -> right 순으로 탐색한다. root를 기점으로 삼각형을 그리며 탐색된다.
Preorder (Root, Left, Right) : 1 2 4 5 3
후위 순회(postorder traversal)
left -> rigt -> root right를 기점으로 삼각형을 그리며 탐색된다.
Postorder (Left, Right, Root) : 4 5 2 3 1
후위 순회는 left에서부터 시작해서 가장 헷갈린다 =ㅅ=
bfs방식 탐색
bfs는 각 노드를 큐에 담아서 순회하기 때문에 레벨 순으로 순회가 가능하다.(따로 구현하진 않음)
Breadth First or Level Order Traversal : 1 2 3 4 5
소스코드
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int value;
node* left;
node* right;
node(int key) : value(key) {
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
};
class BinaryTree {
public:
BinaryTree();
~BinaryTree();
void insert(int key); // 올바른 위치에 노드를 생성해 key를 집어넣는다.
node* find(int key); // 해당 key를 가진 노드가 있는지 찾고 있으면 해당 노드를, 없으면 null을 반환한다.
void preorder_print(); // 전위순회
void inorder_print(); // 중위순회
void postorder_print(); // 후위순회
private:
node* root;
void destroy_tree(node* leaf); // 순회하며 할당된 노드들을 삭제한다.
void insert(int key, node* leaf);
node* find(int key, node *leaf);
void preorder_print(node* leaf); // root -> left -> right
void inorder_print(node* leaf); // left -> root -> right
void postorder_print(node* leaf); // left -> right -> root
};
BinaryTree::BinaryTree() {
root = NULL;
}
BinaryTree::~BinaryTree() {
destroy_tree(root);
}
void BinaryTree::destroy_tree(node* leaf) {
if (leaf != NULL) {
destroy_tree(leaf->left);
destroy_tree(leaf->right);
delete leaf;
}
}
void BinaryTree::insert(int key) {
if (root) insert(key, root);
else root = new node(key);
}
void BinaryTree::insert(int key, node *leaf) {
if (key < leaf->value) {
if (leaf->left) insert(key, leaf->left);
else leaf->left = new node(key);
}
else {
if (leaf->right) insert(key, leaf->right);
else leaf->right = new node(key);
}
}
node* BinaryTree::find(int key) {
return find(key, root);
}
node* BinaryTree::find(int key, node* leaf) {
if (leaf == NULL)return NULL;
if (key < leaf->value) {
return find(key, leaf->left);
}
else if (key == leaf->value) {
return leaf;
}
else {
return find(key, leaf->right);
}
}
void BinaryTree::preorder_print() {
cout << "전위순회 :";
preorder_print(root);
cout << '\n';
}
void BinaryTree::preorder_print(node* leaf) {
if (leaf == NULL)return;
cout << ' ' << leaf->value;
preorder_print(leaf->left);
preorder_print(leaf->right);
}
void BinaryTree::inorder_print() {
cout << "중위순회 :";
inorder_print(root);
cout << '\n';
}
void BinaryTree::inorder_print(node* leaf) {
if (leaf == NULL)return;
inorder_print(leaf->left);
cout << ' ' << leaf->value;
inorder_print(leaf->right);
}
void BinaryTree::postorder_print() {
cout << "후위순회 :";
postorder_print(root);
cout << '\n';
}
void BinaryTree::postorder_print(node* leaf) {
if (leaf == NULL)return;
postorder_print(leaf->left);
postorder_print(leaf->right);
cout << ' ' << leaf->value;
}
int main() {
BinaryTree* tree = new BinaryTree();
tree->insert(10);
tree->insert(6);
tree->insert(14);
tree->insert(5);
tree->insert(8);
tree->insert(11);
tree->insert(18);
tree->insert(13);
node* k = tree->find(5);
if (k)cout << "find!!" << k->value << '\n';
else cout << "null!!\n";
tree->preorder_print();
tree->inorder_print();
tree->postorder_print();
delete tree;
return 0;
}


댓글남기기